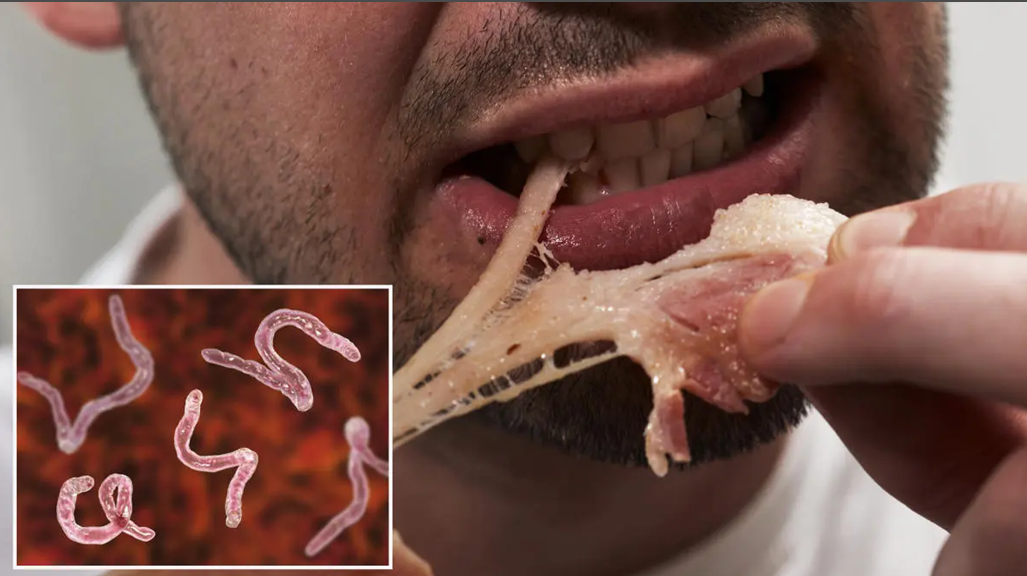
Parasitic worms, or helminths, pose a significant threat to human health, often infiltrating our food supply and causing various diseases. Understanding how these worms enter our food system and the role of medications like Albendazole in controlling them is crucial for safeguarding public health.
Routes of Entry into the Food Supply
Contaminated Soil and Water:
Parasitic worms often thrive in environments with poor sanitation and hygiene. Contaminated soil and water are common sources of helminth eggs and larvae. Crops grown in soil contaminated with human or animal feces can become a vehicle for transmitting these parasites. When fruits, vegetables, or other crops are irrigated with contaminated water, they can harbor parasitic larvae, which then enter the food chain when consumed without proper washing or cooking.
Infected Livestock:
Animals, particularly livestock such as cattle, sheep, pigs, and fish, can become infected with parasitic worms. These animals often ingest contaminated feed or water, leading to internal worm infestations. When humans consume undercooked or raw meat from these infected animals, they can ingest the parasites. Common parasitic infections like Taenia solium (pork tapeworm) and Trichinella spiralis (responsible for trichinosis) are examples of how worms can enter the human body through the consumption of infected meat.
Contaminated Produce:
Produce can also become contaminated with parasitic worms during handling, processing, or transportation. Unsanitary conditions in food processing facilities or markets can facilitate the transfer of helminth eggs from the environment or other infected produce to uncontaminated food items. The risk increases if produce is consumed raw or undercooked, as the parasites are not exposed to heat that could kill them.
Human Handling:
Another significant route of entry for parasitic worms into the food supply is through human handling. Workers in food production, processing, and preparation may carry parasitic worms, especially in regions with high rates of infection. If proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing and using clean tools, are not followed, there is a risk of contaminating food items with helminth eggs or larvae.
Impact on Health
Ingesting parasitic worms can lead to a variety of health issues, ranging from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to severe systemic infections. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. Some parasitic worms can also migrate to other parts of the body, causing more serious conditions such as neurocysticercosis (caused by Taenia solium) or liver damage (caused by Fasciola hepatica, the liver fluke).
The Role of Albendazole in Treatment and Control
Albendazole Supplier is an antiparasitic medication widely used to treat infections caused by various types of parasitic worms. It works by inhibiting the worms’ ability to absorb glucose, leading to their eventual death. Albendazole is effective against a broad spectrum of helminths, including roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes.
Key Uses of Albendazole:
Treatment of Active Infections:
Albendazole Medicine is commonly prescribed to treat infections in individuals diagnosed with helminthiasis. The drug is usually taken orally, often as a single dose or as part of a short course of treatment.
Mass Drug Administration (MDA):
In areas where parasitic worm infections are endemic, Albendazole 400mg is used in mass drug administration programs. These programs aim to reduce the prevalence of helminth infections in at-risk populations, particularly in regions with poor sanitation and high rates of parasitic worm transmission.
Prophylactic Use:
Albendazole is also used prophylactically in some cases, especially for travelers or individuals at high risk of exposure to parasitic worms. By taking the medication before potential exposure, the risk of developing a parasitic infection can be significantly reduced.
Preventive Measures
While Albendazole is effective in treating and controlling parasitic worm infections, prevention remains the most effective strategy for reducing the burden of these parasites in the food supply. Key preventive measures include:
Improving Sanitation:
Ensuring access to clean water and proper sanitation facilities can significantly reduce the risk of soil and water contamination with helminth eggs.
Proper Food Handling and Cooking:
Educating food handlers and consumers about the importance of washing produce, cooking meat thoroughly, and practicing good hygiene can prevent the spread of parasitic worms.
Regular Deworming Programs:
Implementing regular deworming programs for livestock and pets can help reduce the transmission of parasites from animals to humans.
Conclusion
Parasitic worms can enter our food supply through various routes, posing a significant Health risk. While medications like Albendazole are effective in treating infections, preventive measures are essential to minimize the risk of contamination. By improving sanitation, promoting good food handling practices, and supporting deworming programs, we can protect public health and reduce the burden of parasitic worm infections. Read More Medzsupplier Pharma